

Note that this technique works when there are no two customers who have the same credit limits.
#Mysql limit code#
This query returns all customers sorted by credits from high to low: SELECTĬreditLimit DESC Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql )Īs you can see clearly from the output, the result was correct as expected. The clause LIMIT n-1, 1 returns 1 row starting at the row n.įor example, the following finds the customer who has the second-highest credit: SELECTĬreditLimit DESC LIMIT 1, 1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) LIMIT n -1, 1 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) To get the n th highest or lowest value, you use the following LIMIT clause: SELECT select_list 3) Using MySQL LIMIT to get the n th highest or lowest value In this example, the clause LIMIT 10, 10 returns 10 rows for the row 11 – 20. LIMIT 10, 10 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) This query uses the LIMIT clause to get the rows of the second page that include rows 11 – 20: SELECT LIMIT 10 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) This query uses the LIMIT clause to get rows of page 1 which contains the first 10 customers sorted by the customer name: SELECT The last 13th page contains two rows only. Suppose that each page has 10 rows to display 122 customers, you have 13 pages.
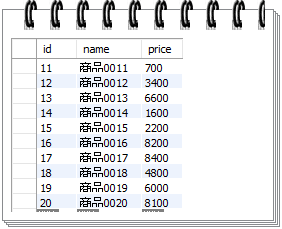
This query uses the COUNT(*) aggregate function to get the total rows from the customers table: SELECT COUNT(*)Ĭustomers Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) +-+ġ row in set (0.00 sec) Code language: JavaScript ( javascript ) To calculate the number of pages, you take the total rows divided by the number of rows per page. For fetching rows of a specific page, you can use the LIMIT clause. When you display data on the screen, you often want to divide rows into pages, where each page contains a limited number of rows like 10 or 20. Try It Out 2) Using MySQL LIMIT clause for pagination To fix this issue, you need to add more columns to the ORDER BY clause to constrain the row in unique order: SELECT First, the ORDER BY clause sorts the customers by credits in low to high.īecause there are more than 5 customers that have credits zero, the result of the query above may lead to an inconsistent result.LIMIT 5 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Similarly, this example uses the LIMIT clause to find five customers who have the lowest credits: SELECT Then, the LIMIT clause returns the first 5 rows.First, the ORDER BY clause sorts the customers by credits in high to low.ORDER BY creditLimit DESC LIMIT 5 Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) This statement uses the LIMIT clause to get the top five customers who have the highest credit: SELECT 1) Using MySQL LIMIT to get the highest or lowest rows We’ll use the customers table from the sample database for demonstration. The following picture illustrates the evaluation order of the LIMIT clause in the SELECT statement: LIMIT offset, row_count Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) Therefore, to ensure the LIMIT clause returns an expected output, you should always use it with an ORDER BY clause like this: SELECT When you add the LIMIT clause to the SELECT statement, the returned rows are unpredictable. In addition to the above syntax, MySQL provides the following alternative LIMIT clause syntax: LIMIT row_count OFFSET offset Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) The LIMIT and ORDER BY clausesīy default, the SELECT statement returns rows in an unspecified order. Therefore, these two clauses are equivalent: LIMIT row_count Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) ( sql ) When you use the LIMIT clause with one argument, MySQL will use this argument to determine the maximum number of rows to return from the first row of the result set.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
